- Competitive pressure: With the increase of the land acquisition limit to 10 000 hectares per owner, small and medium-sized farmers face increased competition from large agricultural holdings. This may result in small farmers being unable to compete in market conditions due to limited resources and lower purchasing power. Consequently, small and medium-sized producers may be forced out of the market. This could also lead to monopolization of land and increase land prices, making it more difficult for small farmers to access land resources.
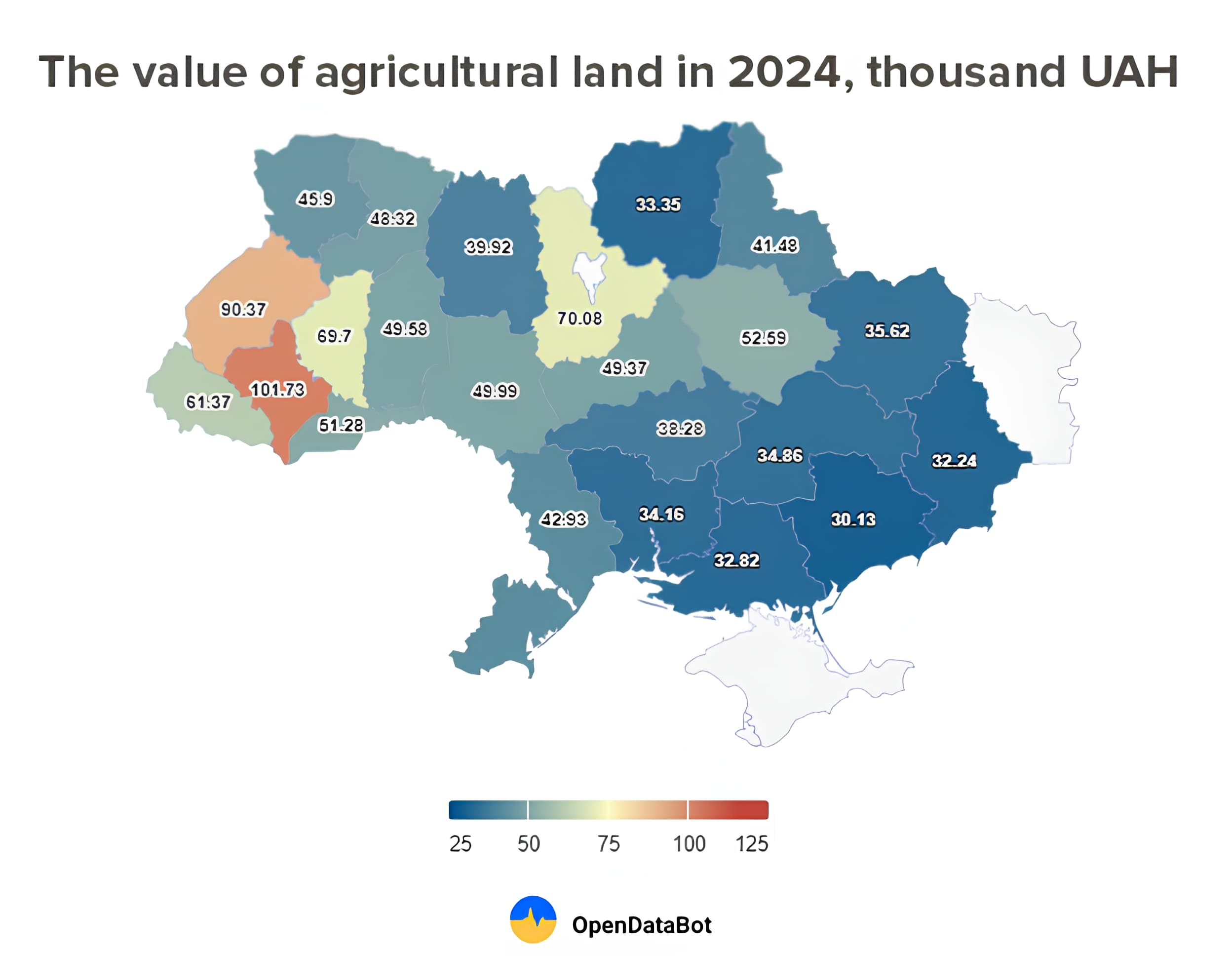
- Financial difficulties: In the context of the current economic crisis and military actions, many small farmers are experiencing financial difficulties. This makes it difficult for them to participate in the land market, especially when the land prices are rising, making them vulnerable to possible land purchases by large players. Thus, as of June 30, 2024, there have been more than 254 thousand transactions for the sale and purchase of Ukrainian agricultural land concluded over the three years of the open land market. According to Opendatabot, over the three years of the land market in Ukraine, 567 322 hectares of agricultural land were purchased at an average price of UAH 41 thousand per 1 hectare. During the entire period of the market’s operation, the largest amount of land was sold in Poltava region — 60.3 thousand hectares. The average price of a hectare of land in the region reached UAH 42.75 thousand. The most expensive land this year was in Ivano-Frankivsk region — UAH 101 thousand per hectare. The lowest prices were in the South and East, at UAH 30-35 thousand per hectare. The weighted average price per hectare in May amounted to UAH 45 thousand, which is 8.2% higher than in April 2024 and 5.6% higher than in March this year.
- Differences in access to resources: Large agriholdings have access to significant financial, technological and managerial resources, which gives them an advantage over small and medium-sized farmers. This may lead to increased centralization and concentration of land in the hands of large agribusinesses.
- Impact on food security: There are concerns that the concentration of land resources in the hands of large agriholdings may affect the country’s food security and the sustainability of small agricultural enterprises. The concentration of land resources in the hands of a few large players may lead to a decrease in product diversity and increased dependence on imports.
- Regional differences: Land prices and market dynamics vary significantly across regions, which can create unequal conditions for farmers in different parts of the country.
- Potential opportunities: Despite challenges, the reform may also provide some opportunities for small and medium-sized farmers, for example, through improved access to finance. For instance, in 2024, there is a EUR 100 million non-repayable financial assistance for farmers in the de-occupied territories — the program is planned to be funded by the European Union, and the State Budget for 2024 provides UAH 200 million to compensate for the cost of domestic agricultural machinery. This program was launched in April 2024, and the “Affordable Loans 5-7-9%” program will continue to operate in 2024. Under this program, farmers can receive loans for the creation of a material and technical base.
Overall, the agrarian reform in Ukraine creates both challenges and opportunities for small and medium-sized farmers, requiring them to adapt to changing market conditions. In the near future, Ukrainian agricultural sector will face a number of opportunities and challenges due to the current economic, political and social environment.
The prospects for agrarian reform include the following:
- Attracting investment: The reform can stimulate foreign investment in the agricultural sector, contributing to its modernization and development. The sources from which investments in the agricultural sector of Ukraine may come or are already coming are:
• The World Bank — provides financing for various projects, including agricultural projects, to stimulate economic development and modernization.
• The European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD) — invests in the agricultural sector of Ukraine through various programs to support small and medium-sized businesses, infrastructure and technology modernization.
• International Monetary Fund (IMF) — provides financial support to stabilize Ukrainian economy, which includes the agricultural sector.
• The United States Agency for International Development (USAID) — finances projects in the agricultural sector of Ukraine aimed at increasing the productivity and efficiency of agricultural production.
• European Investment Bank (EIB) — supports infrastructure projects in Ukraine, including those related to the agricultural sector.
• Rural Development Fund — provides grants and loans for rural development, including agricultural projects.
BDO in Ukraine specialists constantly monitor the grant programs for financing companies in the agricultural sector and are ready to provide support and advice to agricultural enterprises.
- Infrastructure development: Improvements in infrastructure, including logistics and storage, can increase the efficiency and competitiveness of the Ukrainian agri-industry.
- Innovation and technology: The introduction of modern agricultural technologies and innovations can improve the sustainability and productivity of farms. Modern technologies in agriculture are revolutionizing the way farmers grow crops and manage their farms.
Here are some key areas:
1. Internet of Things (IoT) for data collection:
2. Artificial intelligence (AI) for data analysis and forecasts:
3. RTK (Real-Time Kinematic) for precise field operations:
4. Robotics to simplify tasks:
These technologies help farmers use resources efficiently and increase the profitability of their agribusiness.
- Development of cooperatives: Strengthening the cooperative movement can help small farmers improve their economic situation and increase their market share. The following agricultural cooperatives have already been established:
• Agricultural cooperative “Ukraine” — has a large land bank and specializes in growing grain crops, oilseeds and other agricultural products.
• Agricultural cooperative “Progress” — actively cooperates with farmers and provides services for soil cultivation, crops and storage of products.
• Agricultural Cooperative “Zoria” — specializes in the development of agricultural technologies and grain growing.
• Agricultural Cooperative “Spivdruzhnist” — unites farmers for joint purchases of equipment, land cultivation and sales of products.
• Agricultural Cooperative “Nadiia” — actively works to introduce modern agricultural technologies and improve production efficiency.
Considering the above, it can be concluded that, in general, Ukraine’s agricultural sector faces a complex set of challenges and opportunities that require a balanced approach and proactive policies to support sustainable agricultural development.
The material was prepared by the specialists of the Agricultural Sector industrial group at BDO in Ukraine.
If you require professional consultation on the development of your agribusiness, please contact BDO in Ukraine. Our specialists have many years of experience working with agricultural enterprises and are ready to provide you with the necessary support and professional guidance to achieve your business goals. Do not miss the opportunity to utilize our expertise in order to ensure stable growth and development of your enterprise.
*Disclaimer: This information is general information and does not constitute professional advice or service. Before making any decision or taking any action that may affect your finances or operations, you should consult with a qualified professional advisor. Please contact BDO in Ukraine for advice.



